Introduction to NOAA Tide Predictions
For boaters, anglers, and coastal residents, understanding tide predictions is essential for navigation, fishing success, and even shoreline activities. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) provides one of the most accurate and widely used tide prediction systems in the world. But how does NOAA determine tide predictions, and what do they actually mean?
This article explores how NOAA calculates tides, the science behind the predictions, and how you can use them for safe and effective coastal planning.

How NOAA Derives Tide Predictions
NOAA tide predictions are based on a combination of:
- Harmonic Analysis – Uses historical tidal data to identify predictable tidal patterns.
- Astronomical Influences – Factors in the gravitational forces of the moon and sun.
- Meteorological Conditions – Considers wind, atmospheric pressure, and other short-term influences.
- Water Level Observations – Real-time monitoring of tide stations across the U.S.
Harmonic Analysis: The Backbone of Tide Predictions
At the core of NOAA’s tide predictions is harmonic analysis. This method examines decades of historical water level data to identify recurring patterns influenced by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun.
Each tide station records water levels continuously, analyzing multiple tide components called harmonic constituents—over 37 different tidal cycles influence water movement.
The Role of the Moon and Sun in Tide Predictions
Tides occur due to the gravitational interaction between the Earth, moon, and sun. The most significant factors include:
- Lunar Day (24 hours, 50 minutes): The moon’s orbit around Earth causes a shift in the tidal cycle.
- Spring vs. Neap Tides:
- Spring Tides (Higher Highs, Lower Lows): Occur during full moons and new moons when the Earth, moon, and sun align.
- Neap Tides (Moderate Tides): Occur when the moon is at a right angle to the Earth-sun alignment, producing less extreme tides.
Meteorological Conditions That Affect Tides
While NOAA’s tide predictions primarily rely on astronomical factors, they also consider weather conditions that can alter water levels. These include:
- Strong Winds (Onshore vs. Offshore): Can raise or lower tides unexpectedly.
- Storm Surges: Low-pressure systems (hurricanes, nor’easters) can cause significant temporary water level changes.
- El Niño & La Niña: Climate patterns that influence global sea level fluctuations.
NOAA incorporates real-time observational data from tide stations to adjust for these short-term weather effects.
How to Use NOAA Tide Predictions
NOAA provides free, detailed tide predictions via their website:
👉 NOAA Tides & Currents
Key Features of NOAA’s Tide Predictions:
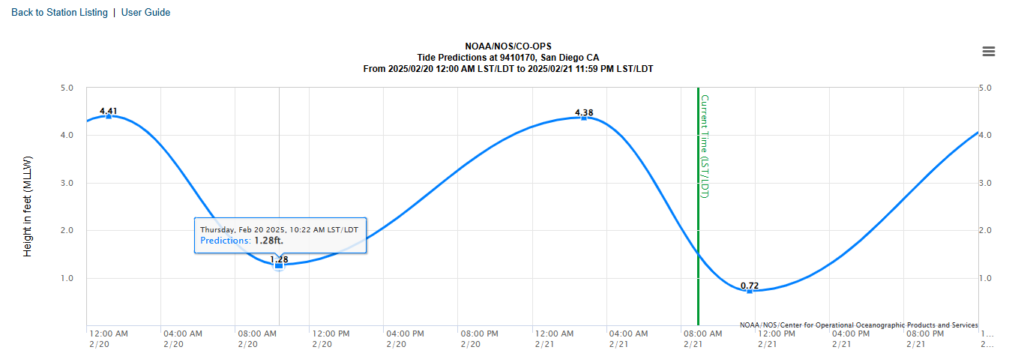
- Daily & Hourly Tide Charts – Visual graphs showing high and low tides.
- Long-Term Tidal Predictions – Data available years in advance for planning.
- Real-Time Water Level Reports – Shows actual conditions at tide stations.
- Currents & Tidal Datums – Helps mariners, fishers, and coastal engineers understand water flow.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using NOAA Tide Predictions
Example: Planning a fishing trip using NOAA’s tide data.
- Visit the NOAA Tides Website and enter your location.
- Check the Tide Chart to identify high and low tides for the day.
- Look at the Moon Phase to see if you are near a Spring or Neap Tide.
- Check Weather Forecasts for wind speed and barometric pressure changes.
- Plan Your Fishing Time—fish often bite best during rising and falling tides.
- Monitor Real-Time Updates for any unexpected tidal shifts.
Common Tide Myths & Misconceptions
Myth #1: Tides Are the Same Everywhere
Fact: Tides vary greatly by location due to coastline shape, ocean depth, and local weather.
Myth #2: High Tide Always Happens at the Same Time Every Day
Fact: Because the lunar day is 24 hours and 50 minutes, high tide shifts roughly 50 minutes later each day.
Myth #3: The Moon Is the Only Factor Affecting Tides
Fact: The sun, wind, ocean currents, and atmospheric pressure also impact tides significantly.
How Climate Change Affects Tides
Climate change is causing global sea levels to rise, which directly impacts tide predictions.
Key Climate-Related Tidal Changes:
- Higher High Tides & Lower Low Tides: Due to shifting oceanic currents and melting polar ice.
- Increased Flooding During High Tides: “King Tides” are becoming more frequent.
- Stronger Storm Surges: Warmer oceans fuel larger hurricanes, intensifying tidal effects.
NOAA continues to adjust tide models to account for these climate-driven changes.
Why NOAA Tide Predictions Matter for Boaters and Anglers
For Boaters:
- Docking & Passage Planning: Avoid getting stuck in shallow waters.
- Bridge Clearance: Know the best times for safely passing under bridges.
- Fuel Efficiency: Plan routes with tidal currents to conserve fuel.
For Anglers:
- Fish Movement: Many species feed more aggressively during tide shifts.
- Best Fishing Times: Peak bite windows often align with incoming (flood) tides.
- Shore & Surf Fishing: Know when the best water levels will occur.
Final Thoughts: Using NOAA Tides for Smarter Coastal Planning
NOAA’s tide predictions are an indispensable tool for boaters, anglers, and coastal communities. By understanding how tides are derived—through astronomical cycles, harmonic analysis, and real-time observations—you can make smarter, safer decisions on the water.
📌 For official tide charts and real-time updates, visit:
🔗 NOAA Tides & Currents
Learn more about the difference in tidal regions here:
West Coast NOAA Tides Explained
Gulf of America (Mexico) Tidal Information